- Free delivery
- Oak caterpillar
- Contact us
- Professionnal work place
- Other pests
-
![ACA - Acarien.info, products against mites]() Acariens Acarien.info, products against mites
Acariens Acarien.info, products against mites -
![ANT - Acarien.info, products against mites]() Anthrène des tapis Acarien.info, products against mites
Anthrène des tapis Acarien.info, products against mites -
![ARA - Acarien.info, products against mites]() Araignee Acarien.info, products against mites
Araignee Acarien.info, products against mites -
![ARE - Acarien.info, products against mites]() Arrosage écologique Acarien.info, products against mites
Arrosage écologique Acarien.info, products against mites -
![CAF - Acarien.info, products against mites]() Cafards et Blattes Acarien.info, products against mites
Cafards et Blattes Acarien.info, products against mites -
![CAR - Acarien.info, products against mites]() Carpocapse (vers des fruits) Acarien.info, products against mites
Carpocapse (vers des fruits) Acarien.info, products against mites -
![CRO - Acarien.info, products against mites]() Charancon rouge du palmier Acarien.info, products against mites
Charancon rouge du palmier Acarien.info, products against mites -
![CHI - Acarien.info, products against mites]() Chats-Chiens Acarien.info, products against mites
Chats-Chiens Acarien.info, products against mites -
![LCV - Acarien.info, products against mites]() Chauve souris Acarien.info, products against mites
Chauve souris Acarien.info, products against mites -
![CHE - Acarien.info, products against mites]() Chenille Processionnaire Acarien.info, products against mites
Chenille Processionnaire Acarien.info, products against mites -
![DES - Acarien.info, products against mites]() Desherbage Acarien.info, products against mites
Desherbage Acarien.info, products against mites -
![DVB - Acarien.info, products against mites]() Désinfection-Virus-Bacterie Acarien.info, products against mites
Désinfection-Virus-Bacterie Acarien.info, products against mites -
![DIU - Acarien.info, products against mites]() Destructeur Insectes UV Acarien.info, products against mites
Destructeur Insectes UV Acarien.info, products against mites -
![EPI - Acarien.info, products against mites]() Equipement Protection Individuelle Acarien.info, products against mites
Equipement Protection Individuelle Acarien.info, products against mites -
![FNE - Acarien.info, products against mites]() Fouines Acarien.info, products against mites
Fouines Acarien.info, products against mites -
![FOU - Acarien.info, products against mites]() Fourmis Acarien.info, products against mites
Fourmis Acarien.info, products against mites -
![GUE - Acarien.info, products against mites]() Guêpes - Frelons Asiatique Acarien.info, products against mites
Guêpes - Frelons Asiatique Acarien.info, products against mites -
![ENG - Acarien.info, products against mites]() Les Engrais Acarien.info, products against mites
Les Engrais Acarien.info, products against mites -
![LIM - Acarien.info, products against mites]() Limaces Acarien.info, products against mites
Limaces Acarien.info, products against mites -
![TAU - Acarien.info, products against mites]() Lyon Taupe Acarien.info, products against mites
Lyon Taupe Acarien.info, products against mites -
![INS - Acarien.info, products against mites]() Maisons Insectes Acarien.info, products against mites
Maisons Insectes Acarien.info, products against mites -
![MAT - Acarien.info, products against mites]() Materiel de traitement Acarien.info, products against mites
Materiel de traitement Acarien.info, products against mites -
![MEP - Acarien.info, products against mites]() Mérule Acarien.info, products against mites
Mérule Acarien.info, products against mites -
![MIN - Acarien.info, products against mites]() Mineuse du Marronnier Acarien.info, products against mites
Mineuse du Marronnier Acarien.info, products against mites -
![MIT - Acarien.info, products against mites]() Mites des Vêtements - Alimentaire Acarien.info, products against mites
Mites des Vêtements - Alimentaire Acarien.info, products against mites -
![MOC - Acarien.info, products against mites]() Mouche cerise Acarien.info, products against mites
Mouche cerise Acarien.info, products against mites -
![OLI - Acarien.info, products against mites]() Mouche de l olive Acarien.info, products against mites
Mouche de l olive Acarien.info, products against mites -
![SUZ - Acarien.info, products against mites]() Mouche suzukii Acarien.info, products against mites
Mouche suzukii Acarien.info, products against mites -
![MDT - Acarien.info, products against mites]() Mouche-du-terreau Acarien.info, products against mites
Mouche-du-terreau Acarien.info, products against mites -
![MOU - Acarien.info, products against mites]() Mouches Acarien.info, products against mites
Mouches Acarien.info, products against mites -
![MTQ - Acarien.info, products against mites]() Moustique Acarien.info, products against mites
Moustique Acarien.info, products against mites -
![NEM - Acarien.info, products against mites]() Nématodes Acarien.info, products against mites
Nématodes Acarien.info, products against mites -
![NIC - Acarien.info, products against mites]() Nichoirs et Abris Acarien.info, products against mites
Nichoirs et Abris Acarien.info, products against mites -
![PAL - Acarien.info, products against mites]() palmiers Acarien.info, products against mites
palmiers Acarien.info, products against mites -
![PAY - Acarien.info, products against mites]() Papillon du palmier Acarien.info, products against mites
Papillon du palmier Acarien.info, products against mites -
![PHE - Acarien.info, products against mites]() Phéromone bio Acarien.info, products against mites
Phéromone bio Acarien.info, products against mites -
![PGE - Acarien.info, products against mites]() Pigeon Acarien.info, products against mites
Pigeon Acarien.info, products against mites -
![POU - Acarien.info, products against mites]() Poux rouges du Poulailler Acarien.info, products against mites
Poux rouges du Poulailler Acarien.info, products against mites -
![PDC - Acarien.info, products against mites]() Protection du cheval Acarien.info, products against mites
Protection du cheval Acarien.info, products against mites -
![PCR - Acarien.info, products against mites]() Pucerons Acarien.info, products against mites
Pucerons Acarien.info, products against mites -
![PUC - Acarien.info, products against mites]() Puces Acarien.info, products against mites
Puces Acarien.info, products against mites -
![PUL - Acarien.info, products against mites]() Pulvérisateur Acarien.info, products against mites
Pulvérisateur Acarien.info, products against mites -
![PUN - Acarien.info, products against mites]() Punaise de Lit Acarien.info, products against mites
Punaise de Lit Acarien.info, products against mites -
![PUR - Acarien.info, products against mites]() Purin Acarien.info, products against mites
Purin Acarien.info, products against mites -
![PYR - Acarien.info, products against mites]() Pyrale du buis Acarien.info, products against mites
Pyrale du buis Acarien.info, products against mites -
![SER - Acarien.info, products against mites]() Serpents Acarien.info, products against mites
Serpents Acarien.info, products against mites -
![SDA - Acarien.info, products against mites]() Soin des arbres Acarien.info, products against mites
Soin des arbres Acarien.info, products against mites -
![SDV - Acarien.info, products against mites]() Soin des végétaux Acarien.info, products against mites
Soin des végétaux Acarien.info, products against mites -
![SOU - Acarien.info, products against mites]() Souris - Rat - Campagnol - Rongeur Acarien.info, products against mites
Souris - Rat - Campagnol - Rongeur Acarien.info, products against mites -
![STO - Acarien.info, products against mites]() Stop Odeur Acarien.info, products against mites
Stop Odeur Acarien.info, products against mites -
![TIG - Acarien.info, products against mites]() Tigre du Platane Acarien.info, products against mites
Tigre du Platane Acarien.info, products against mites -
![CPT - Acarien.info, products against mites]() Tout Pour Le Compost Acarien.info, products against mites
Tout Pour Le Compost Acarien.info, products against mites -
![TPG - Acarien.info, products against mites]() Tout Pour Mon Gazon Acarien.info, products against mites
Tout Pour Mon Gazon Acarien.info, products against mites -
![PRU - Acarien.info, products against mites]() Ver de la prune Acarien.info, products against mites
Ver de la prune Acarien.info, products against mites -
![VRI - Acarien.info, products against mites]() Vrillette Acarien.info, products against mites
Vrillette Acarien.info, products against mites
-
SOLUNEMA Cutworms (moth caterpillars) - 50 million Nematodes Steinenerma Carpocapsae SC
Disponibilité : En stock
SOLUNEMA - Greyworms 50 million (noctuid caterpillars) - SC
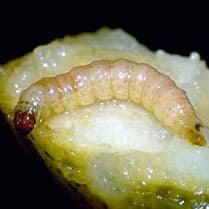
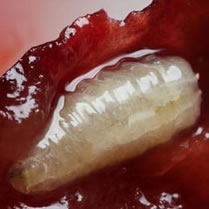
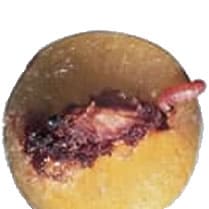
Cutworms, also known as moth caterpillars, are harmful insects belonging to different species of moths. These caterpillars feed on various plants, causing considerable damage in gardens and crops.
Cutworms have a fleshy, cylindrical body, usually dark gray or brown in color. They can measure from a few centimeters to several centimeters in length, depending on the species. The caterpillars move at night and usually hide during the day in the ground, under leaves or in other plant shelters.
The damage caused by cutworms is mainly due to their voracious appetite. The caterpillars feed on the leaves, stems, flowers and even the roots of plants. They may nibble on leaves down to the midrib, leaving behind chewing marks and shredded leaf pieces. Infested plants may appear defoliated, weakened and may even die if the infestation is severe.
Cutworms are known to be polyphagic, which means they can attack many plant species, including vegetables, flowers, fruit trees and ornamentals. Their life cycle includes several stages of development, ranging from egg to caterpillar, then to nymph and finally to adult butterfly.
How to use nematodes to treat white grubs?
1. Identify the problem
Signs of cutworms are often visible on plants. Caterpillars feed on leaves, stems and flowers, leaving chewing marks, shredded leaf pieces and sometimes droppings. Infested plants may appear defoliated, weakened and may even die if the infestation is severe. The presence of cutworms can vary depending on the species and plants affected. Moth caterpillars usually hide in the ground, under leaves or in other plant cover during the day, which makes their detection more difficult. However, it is possible to spot their presence by carefully examining the affected parts of the plants and looking for the caterpillars themselves.
2. When to treat?
The most common treatment time is usually in the spring and fall, when the cutworm caterpillars are most active. It is recommended to apply the nematodes at the beginning of these seasons, when the caterpillars are still small and more susceptible to infection by the nematodes.
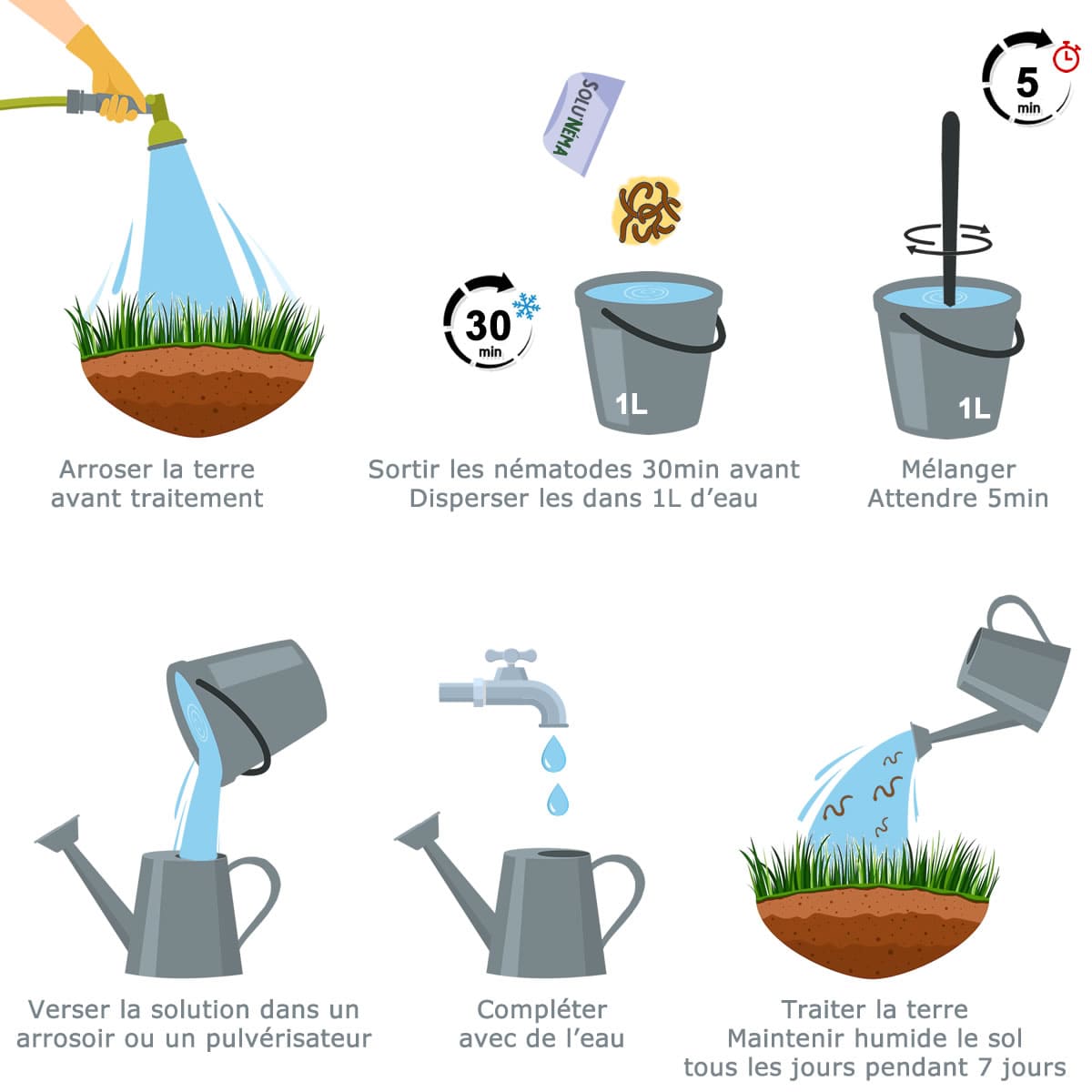
3. Preparation of nematode solution
Begin by diluting the entire sachet of nematodes in a small container of clean water at room temperature. Mix well, any lumps are not very serious. Then, pour this preparation into a watering can or sprayer and add 10 liters of water at room temperature (between 15°C and 25°C). Mix again.
4. Application by spraying or watering nematodes
Make sure the soil is slightly moist before applying the nematodes. This will make it easier for them to move and find the cutworms. Use a watering can or sprayer to spread the nematode solution over the infested area or the entire surface of the garden.
5. Continue watering
Nematodes need a moist environment to survive. To maintain their effectiveness, continue to regularly water the crop lightly. Nematodes need moisture to move through the soil and find cutworms.
6. Monitor results
Steinernema Carpocapsae nematodes work by infecting cutworms and killing them inside their bodies. You should see a gradual decrease in the cutworm population over time. Carefully monitor the condition of the plants to assess the effectiveness of the treatment. If necessary, you can repeat the application of the nematodes to ensure complete control of the infestation.
How do nematodes work?
Nematodes move through the soil in search of larvae to parasitize them.
When they find them, they naturally enter the larva and release symbiotic bacteria. These bacteria transform the tissues into assimilable nutrients allowing the nematodes to feed, grow and reproduce. This kills the cutworm within days of infection.
Composition
86% Steinernema Carpocapsae. 14% biodegradable inert carrier
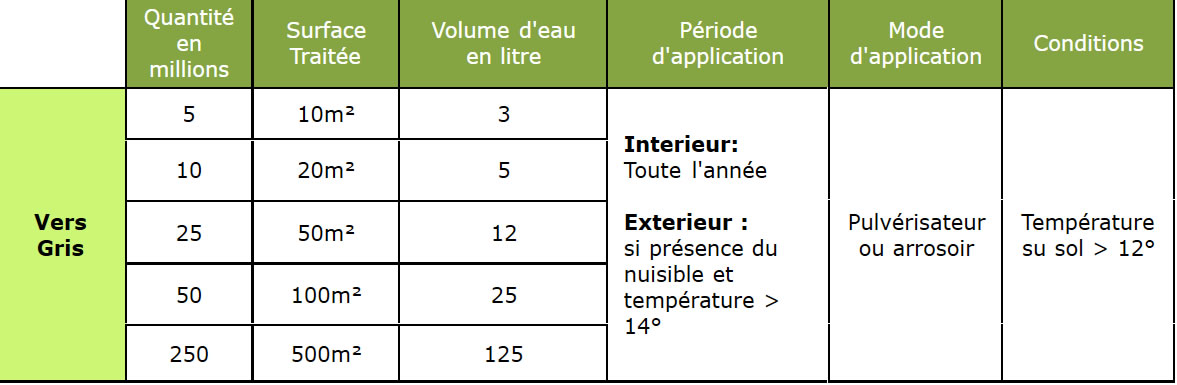
Dosage
IMPORTANT
- Store cool at 4-6°C (do not freeze) in the refrigerator after receipt until use and protected from light.
- Bring to room temperature for 30 minutes before use.
- To be used as soon as temperatures are above 10° C
- Use early morning or late evening to avoid UV, as nematodes are UV sensitive.
- Keep the soil slightly moist and not soaked for at least 15 days after the treatment.
- Nematodes are not necessarily afraid of heat (<30°C), keeping them cold only aims to plunge them into cryptobiosis, thus keeping them in a state of lethargy.
- At room temperature, the nematodes continue their development. On the other hand, without "food", they will eventually die of "starvation" after about a week.
- Spraying: Remove the filters, use a nozzle with a diameter > 0.5 mm (35 mesh), prefer a high-flow hollow "conical jet" type nozzle.
- Do not keep the solution once diluted in water, the nematodes would eventually die of asphyxiation.
You have no products in your basket
Continuer mes achats| Cart Summary | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Subtotal : | 0.00 € | ||||||||
|
|
|||||||||
| Total : | 0.00 € | ||||||||








Over-Ear Headphone
$120 $200
Lorem ipsum, dolor sit, amet consectetur adipisicing elit. Ipsum non facilis corporis modi consequatur. Iure perferendis dicta illum deleniti veritatis vero tempora maxime ducimus quaerat, iusto omnis magni doloribus. Repellat exercitationem odio amet sit.